What is Acid Mine Drainage (AMD)?
Acid mine drainage (AMD) is produced from mining coal or mineral deposits. The acidic nature of the water is caused by the oxidation of the mineral pyrite (FeS2), which contains iron and sulfur. Pyrite is exposed to and reacts with air and water to produce sulfuric acid and dissolved iron (as well as dissolved aluminum and other minerals in some cases). Pyrite is found in coal, coal overburden, and mine waste piles. The iron can precipitate (come out of solution), which produces the red, orange, or yellow tint to the water (termed “yellow boy”).
In addition, other environmental impacts include disruption to the growth and reproduction of aquatic plants and animals, decrease or loss of fish species, and even contamination of surface and groundwater drinking supplies.
How is Acid Mine Drainage Remediated?
AMD is remediated with both active and passive treatment systems.
Active treatment involves mechanical systems that add alkaline chemicals to the discharge to neutralize the acidity and cause metals to precipitate quickly. The chemicals used include lime, soda ash, or ammonia. Passive systems include open limestone channels, anoxic limestone drains, diversion wells, and limestone sand. Additionally, passive systems to remove metals include aerobic wetlands, anaerobic wetlands, SAPS (Successive Alkalinity Producing Systems), limestone ponds, bioremediation, and resource recovery.
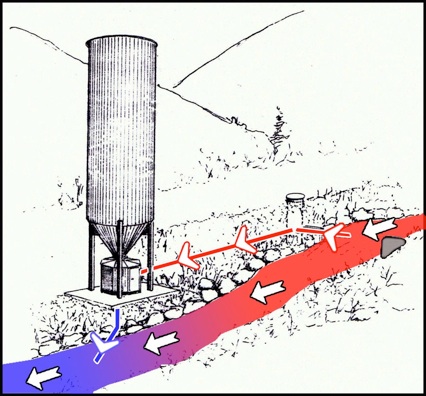
The Lime Doser System is an Active Treatment that works very well using pre-measured amounts of hydrated lime that are added to the discharge by water power only. The hydrated lime is a dry powder made by treating quicklime with water, which converts oxides to hydroxides.
Learn More About Our Products | See What Our Clients Say